Getting Started with Email Deliverability
Before sending your carefully-crafted email campaigns, it's important to first learn a few basic ideas and rules of email marketing to ensure your campaigns are successful. To achieve good open and click-rates, and to avoid your emails from landing in the spam folder, you must first earn your contacts' trust .
The factors that play an important role in improving your email deliverability, while also gaining the trust of contacts are:
Domain Authentication
Before an email gets delivered, it is first validated to ensure it's coming from a safe origin. With phishing attacks happening every day all over internet, it's important to prove how safe and secure you are. That leads us to an important question. How to prove your emails are from a safe origin?
Any email you send has to first be authenticated. Based on the status of authentication, emails get classified and then delivered to the inbox (if authenticated properly), quarantined, or sent to the spam folder.
Domain authentication includes:
• SPF (Sender Policy Framework) - to authorize the sending source,
• DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) - attaches Domain Key to encrypt the message and is inclusive of SPF
• DMARC (Domain- based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conforming) - prevents illegitimate usage of domain name in sender address.
By default, Zoho Campaigns performs authentication for all email sending domains. We highly recommend you to authenticate your domain to avoid phishing attacks.
✔ SPF

"The Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is an open standard specifying a technical method to prevent sender address forgery. "
An SPF is a record that manages IP addresses which can send emails from your domain. It is the authentication of the sending source. If an email is sent from an IP address that is not on your list, it'll be treated as if it's from an untrusted network. This is a common reason many emails land in the spam folder.
If you are sending emails through Zoho Campaigns, then you have to authorize Zoho Campaigns to send emails on your behalf. Learn more .
✔ DKIM

"DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) lets an organization take responsibility for a message that is in transit. The organization is a handler of the message, either as its originator or as an intermediary. Their reputation is the basis for evaluating whether to trust the message for further handling, such as delivery." Source: DKIM
In ancient days, when a letter was sent from a high-ranking official or emperor, it would have been sealed. If the seal was unbroken, the recipient had full confidence that the message had not been altered in any way. Similarly, when emails are sent across the internet we must make sure that the email is not intercepted or altered before it is received.
DKIM encryptions confirm that a message sent from the sender is not affected and is identical to the original message. Learn more .
✔ DMARC

"DMARC, which stands for “Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance”, is an email authentication, policy, and reporting protocol. It builds on the widely deployed SPF and DKIM protocols to improve and monitor protection of the domain from fraudulent email." Source: DMARC
DMARC makes it impossible for a user to see a fake/fraudulent email from a brand’s domain name. In short, it helps conserve a domain's reputation.
This is the latest protocol that was recently formulated to ensure good deliverability to reputable inbox providers.
Complying to DMARC policy is an added advantage. DMARC tells ISPs and ESPs what actions emails can take without passing SPF and DKIM.
Emails sent from authenticated sender domains will build good reputation with email filters.
Domain
✔ Sender Domain
We recommend you use an email address with either your organization's domain or sub-domain. For example, patricia@zylker.com or patricia@news.zylker.com .
The domain from your official website and the domain you use for sending campaigns must be related. For example, if your website is www.zylker.com then your email address should be something like bob@zylker.com or bob@email.zylker.com . However, if you use something like bob@zillum.com , then your contacts will find it difficult to recognize you.
The email recipients should be able to easily recognize the sender address and the company attached to it.
✔ Domain Blacklist check-up
Before sending an email, make sure your domain isn't blacklisted. Blacklisting depends on the sender's domain reputation. You can check the reputation of your domain at Sender Score , SenderBase , or other similar services.
Check your domain reputation with leading anti-spam or blacklist service providers such as Spamhaus , Sorbs , Spamcop and others.
If your domain is blacklisted, contact the concerned anti-spam service provider and ask to delist it, or if possible, try to whitelistit .
Contacts
Contact management is one of the most important factors for succesful email campaigning. Having more contacts is not necessarily the goal, but managing them properly and efficiently to reach the right audience is.
✔ List segmentation
Categorizing your contacts based on the people you specifically want to target for a campaign is list segmentation.
Let's imagine that you want to invite your contacts to a webinar on pencil making. Your mailing list may have pencil makers as well as box makers, laptop makers and pen makers.
Your email would be useful to pencil makers but the others would ignore it or even mark it as spam. Such scenarios happen often in email marketing, so it's really important to segment your contacts.
List segmentation is based on target marketing. A target market is a group of people considered likely to buy a product or a service. A target market consists of customers who share similar characteristics like age, location, income, and lifestyle, to which a business directs its marketing efforts and sells its products.
In the infograph below, we've explained the types of list segmentation with illustrations,

Your opt-in list may contain contacts with whom there might be a communication gap in a significant duration (more than 6 months). When you send an email now they may not recognize you and hence may mark it as spam. Send them re-engagement emails and while doing so, introduce yourselves. If they are unresponsive or uninterested, remove them from your list.
✔ Email campaign frequency
Sending emails regularly is great, but if you send them too frequently, like once a day, your recipients may get annoyed or lose interest.
If your emails flood your recipients' inboxes, they may mark it as spam, unsubscribe, or report a complaint.
To avoid this, choose a pattern in your Zoho Campaigns Settings (if you are an admin).
- Per day not more than one email can be sent.
- Per week 2 - 3 emails can be sent
- Per month maximum of 8 emails can be sent.
The frequency interval between two campaigns should be at least one day. If you want to send a campaign, but your email limit has exceeded, then the admin from your organization will have to make changes to the settings.
To learn how to set email limits, click here .
✔ Bounces
Bounces occur when sent emails can't be delivered. When this happens, the email server sends you an error message describing why the email was bounced.
We've separated the possible reasons for bounces into categories in the image below:
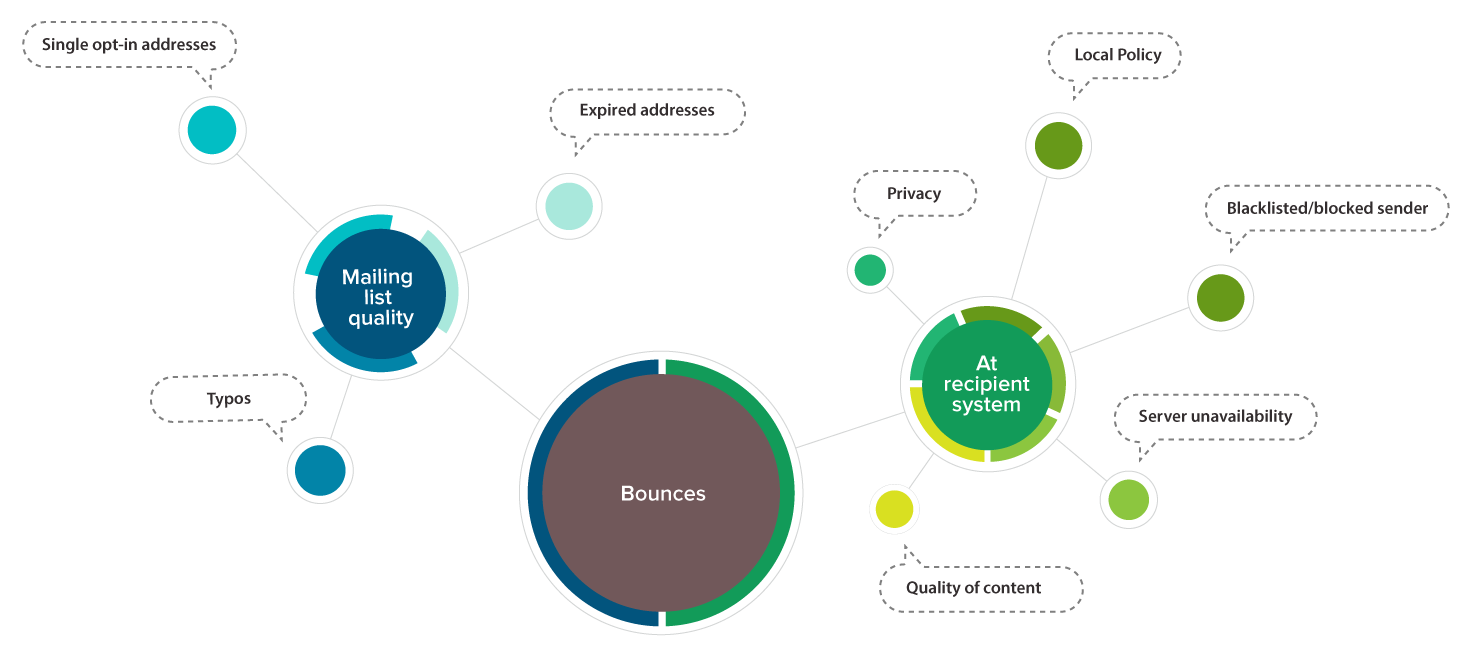
Bounces can occur due to a poor-quality mailing list, or any of several factors at the recipient end.
Mailing list quality
- Typos
Typos may occur when email addresses are manually added to a list. You can easily avoid this by having a double opt-in subscription method.
- Single opt-in addresses.
If you use a single opt-in subscription method, it's impossible to check whether contacts have given a valid email address. Some people give dummy or fake email addresses while signing up, which will increase your bounce rate if you don't catch them. These fake subscription attempts can be prevented by requiring the recipient to confirm their email address through the double opt-in subscription method.
- Expired email addresses
Email addresses which were once active but have since expired will result in a bounce. For example, when an employee leaves an organization, their email address typically expires.
At recipient system
- Privacy
Most email systems not only filter spam, but also allow recipients to define their privacy settings and reject certain types of messages.
For example, someone may note that they don't want emails related to banking, so if a marketer sends them an email related to loans, it'll be bounced by the email server.
- Local policy
When an email server encounters an email which doesn’t comply with policy settings, it is bounced. The policy of recipient system could have restrictions on the rate incoming emails per day, volume of email reipients, etc.
- Blacklisted/blocked sender
If the domain of your sender address is blacklisted by a recipient's email server, or if it triggers suspicion, any email you send to that server will be bounced. Check your domain reputation with a leading anti-spam or blacklist service provider such as Spamhaus, Sorbs, or Spamcop.
If your sender address is blacklisted, resolve it by contacting the email server. You can also work on the situation that caused you to be blacklisted (for instance, high bounces).
To learn how to avoid getting blacklisted, click here .
- Server unavailability
Email servers may block your messages for technical reasons such as "box size full”, “server busy", "unavailable to respond”, and “resources temporarily unavailable.”
- Quality of content
If an email has phrases that resemble spam trigger words, then the recipient's email server will bounce it. Avoiding such words when composing email subject lines and content will help you avoid unnecessary bounces.
Using URLs from blacklisted domains is unsafe. If you include blacklisted URLs in your messages, the recipient system can bounce them.
Some recipient systems consider lengthy email content to be spam. The server may bounce such emails before they even get to the recipient.
To learn how to avoid bounces, click here .
✔ Email throttling
If you're sending emails to a large number of contacts in the first attempt, then suspicion will arise among email recipient systems.
Let's say you have a million contacts and many of your contacts belong to one or few inbox providers (for example, 600,000 of your million contacts are Gmail users and 200,000 contacts are Yahoo! users). Then the following scenario will occur.
You are new to that recipient system, say, Gmail or Yahoo!, and you are sending large number of emails in the first attempt. The recipient system may view that as suspicious as you don't have any footprints with their system.
Until you build good domain reputation with the recipient system, it may defer your emails.
The best solution to this is to segment your mailing list and to gradually increase the number of email recipients.
Content
Email content includes the following:
- Subject
- Message to be conveyed to contact
- Sender logo
- Images
- Footer
✔ Subject
Email subject is like the head of a body. It's one of the first things your contacts observe when they receive an email.
Open rates of your emails depend greatly on your subject line. That's why it's crucial to spend a lot of time crafting this part of your email.
In general, the subject needs to be:
- Short and crisp
- Free of spelling or grammar errors
- Devoid of false promises
To learn more on crafting subject line, click here .
✔ Sender Logo
When you send emails to your contacts, it's important that they recognize you easily. Including your logo in email content gives easy brand recognition to the contacts.
Your organization more likely has a standard format/layout when positioning your logo, so make sure to follow that position and follow it in all your emails.
✔ Email Message
The purpose of sending emails is to convey the message you want to deliver to your contacts. It's important to position your content in such a way that it doesn't create suspicion among spam filters and recipients.
That's why Zoho Campaigns reviews your content before sending it to recipients.
✔ Images
Image-text ratio (40:60) should be maintained.
Use clear images which are easily loadable for your contacts.
✔ Footer
Each business related communication must contain a legal notice. This information may be included in the email as a whole (this method is preferred) or by adding a URL.
- Name of the sender or company name
- Authorized representatives
- Postal address of the sender
- Telephone number, fax number or electronic contact form
- The sender's email address
- Commercial, cooperative, association or partnership register number
- Naming of the publisher or person responsible for the content of the email
- If available: Tax Identification Number or business identification number
This information must be:
- Easily perceptible
- Directly accessible
- Permanently available

If you have a disclaimer make sure to include it at a specific location that is constant across all emails.
Include " Unsubscribe " option clearly in all your campaigns.
Keep footer in resemblance with the footer in your official website.
✔ Using URLs

- If your email content contains any URLs, make sure that they are from domains that are easily recognizable to your contacts . Using non-business domains leads to suspicion among spam filters and contacts. It may result in emails getting marked as spam.
Example: If your sender address is abc@exampledomain.com , then the URLs you use can be from domains such as, example.domain.com, exampledomain.com, example.com, etc, but not from non-business domains such as hello.com, something.com, etc.
- The URLs you use in your content should not have multiple redirections . One or two redirections are acceptable but not any more than that.
- Using shortened URLs from public services is not advisable . They're vulnerable to many attacks and may get blacklisted easily.
✔ URL Blacklist Checkup
Verify whether your URLs are being blacklisted before sending emails. If they are blacklisted then you have to "de-list" them. Check reputation of URLs to be used with leading anti-spam or blacklist service providers such as Spamhaus , Sorbs , Spamcop and others.
Sending practices
Your contacts may have their email addresses in various inbox providers like Gmail, Yahoo!, Outlook, etc. To improve your deliverability, you should familiarize yourself with a few best practices on sending emails to various inbox providers.
Gmail, Yahoo!, Outlook, and other inbox providers analyze your domain reputation and the history of spam markings in your emails before they get delivered. And then on checking your email content, spam filters at system level (by ESPs and ISPs) classify your emails.
Your contacts may also mark your emails as spam at contact level . Based on your contacts' responses, spam filters maintain a reputation for sender email address and domain. A good domain reputation means good email deliverability rate.
To keep your domain reputation good with these inbox providers, it is essential to have good rapport with your contacts. Remember, every single spam marking by your contacts gradually reduces your reputation.
- Zoho Campaigns strongly recommends you follow permission-based email marketing . Ensure that all of your contacts are opt-in.
- In email content and subject, avoid words such as buy, order, discount, clearance, dear friend, as seen on, please help, free, offer, desperate, additional income, etc.
- Ensure that your subject and content are relevant to each other. If the subject doesn't convey the message you actually intended for your contacts, they get mislead and mark your email as spam.If your contacts are Gmail users, look through the pages given below and learn more on how Gmail marks an email spam with respect to:
Getting your emails delivered in Gmail not only means getting them through spam filters but also getting into the Primary tab .
Emails in Primary tab grab more attention from recipients.
If your emails end up in Promotions Tab, then the open rates and click rates will be significantly less. Promotions tab is where many marketing emails land.
To learn how to make your emails land in Gmail's Primary tab, click here .
Conclusion
Successful email marketing campaigns begin and end with preparation. Not only do you need an organized mailing list along with creative and valuable content, but you also have to make sure every campaign satisfies a number of conditions before you click 'send'.
At Zoho Campaigns, we hope all elements we discussed here will give you a broader perspective to improve your email deliverability while decreasing bounces, unsubscribes, complaints, and spam markings.
Related Articles
Getting Started with Email Deliverability
Before sending your carefully-crafted email campaigns, it's important to first learn a few basic ideas and rules of email marketing to ensure your campaigns are successful. To achieve good open and click-rates, and to avoid your emails from landing ...Getting Started
There's so much to social media marketing—scheduling and publishing content, listening to and engaging with your audience, and analyzing performance across social networks. We understand that your presence on social media is an integral part of ...Getting Started
There's so much to social media marketing—scheduling and publishing content, listening to and engaging with your audience, and analyzing performance across social networks. We understand that your presence on social media is an integral part of ...Getting Started With Zoho Vault
Zoho Vault is a password management solution that is part of Zoho's business suite consisting of 40+ apps and trusted by over 50 million users across the globe. It helps individuals, teams, and enterprises to securely store, share, and manage their ...Getting started with Zoho Projects
Zoho Projects is an online project management software that helps you run your business with ease. It stands as a comprehensive solution to your day-to-day problems in project management and adds value to your business by leaps and bounds. Find out ...